PC Maintenance Basics (Keep It Running Good Long-term)
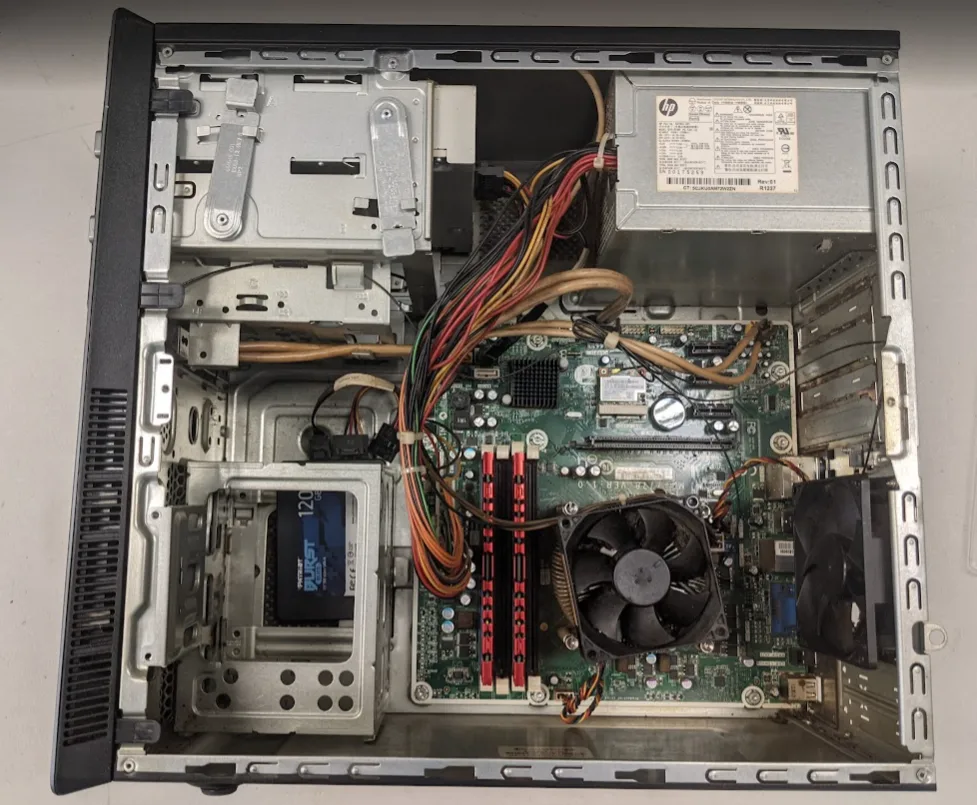

PC maintenance is the ongoing process of keeping your computer clean, updated, and running efficiently. You’re better than fixing problems after they happen. You’re preventing them in the first place. A well-maintained system can last years longer, perform more consistently, and avoid many of the frustrating slowdowns, crashes, and overheating issues that plague neglected machines.
Regular maintenance addresses both hardware and software needs. Physically, this means removing dust, ensuring proper airflow, and checking components for wear. On the software side, it involves keeping your operating system, drivers, and applications up to date while clearing unnecessary files that waste storage and slow performance.
This guide will cover the most important maintenance tasks you can do yourself, from monthly checkups to occasional deep cleans.
Why regular maintenance matters
Neglecting PC maintenance doesn’t just cause minor inconveniences—it can shorten your hardware’s lifespan, create security vulnerabilities, and lead to costly repairs. Dust buildup is one of the most common issues. Over time, it clogs fans and heatsinks, reducing airflow and causing components to overheat. Excess heat accelerates wear on sensitive parts like the CPU, GPU, and power supply, sometimes leading to sudden failures.
On the software side, outdated operating systems and drivers leave your PC open to malware exploits and performance bottlenecks. Even if you aren’t installing new programs regularly, security patches, firmware updates, and driver improvements can fix bugs, optimize performance, and protect against vulnerabilities that attackers actively target.
Regular maintenance also keeps performance consistent. Temporary files, unused programs, and background processes accumulate slowly, but they sap speed and responsiveness. Without periodic cleanups, your PC may feel sluggish even if the hardware is fine.
By setting aside time each month for routine checks, you not only reduce the risk of sudden breakdowns but also extend the life of your investment. A few minutes spent maintaining your system can save hours of troubleshooting later and potentially hundreds of dollars in replacement costs.
Monthly PC maintenance checklist
A consistent maintenance routine is the easiest way to keep your PC running smoothly. Spending 20–30 minutes each month on a few key tasks can prevent most performance and reliability issues. Here’s a quick rundown of what to include:
- Clean temporary files and cache – Use Windows’ built-in Disk Cleanup or Storage Sense, or a tool like CCleaner, to remove leftover files that waste space.
- Update Windows and drivers – Install security updates, firmware patches, and driver updates for your GPU, chipset, and other hardware.
- Check disk health – Use tools like CrystalDiskInfo or the built-in
wmic diskdrive get statuscommand to spot early signs of drive failure. - Run antivirus scans – Even with real-time protection enabled, a full system scan can catch dormant threats.
- Inspect and clean fans/filters – Quickly vacuum or blow out dust from intake filters to maintain airflow.
- Check startup programs – Disable unnecessary apps from launching at boot via Task Manager’s Startup tab.
Following a set schedule ensures these tasks become habit rather than an afterthought. For a printable version and a deeper breakdown of each step, see our Monthly PC Maintenance Checklist (Free Download) guide.
How to clean dust from your PC
Dust is a silent but deadly killer of PC performance. It collects on fans, heatsinks, and filters, restricting airflow and trapping heat inside your case. Over time, this can cause components to throttle performance or even fail. A quick clean every few months—more often in dusty environments—can prevent overheating and extend hardware lifespan.
Before you start, shut down your PC, unplug it from power, and ground yourself to prevent static discharge. Move the system to a well-ventilated area. Remove the side panel, and use short bursts of compressed air to blow dust out of fans, heatsinks, and power supply vents. Hold fan blades still while cleaning to avoid damaging bearings. If your case has removable dust filters, wash them with mild soap and water, then let them dry completely before reinstalling.
For stubborn buildup, a soft brush can loosen debris without scratching components. Avoid household vacuums directly on components—they can create static discharge. After cleaning, ensure all fans spin freely and cables are clear of blades.
For a full, step-by-step cleaning process with visuals and tool recommendations, see our How to Clean Dust from Your PC guide.
How to replace thermal paste
Heads up. This one is a little more involved, So don’t be afraid to chicken out and call a pro if you don’t feel right about really digging into the inner workings of your hardware. Plus, you don’t need to worry about it unless your computer is OLD (like almost vintage). Still, this can help you big time if you care to dive in, especially when it comes to maxing out games and heavy apps.
Thermal paste fills microscopic gaps between a CPU or GPU heat spreader and its cooler, ensuring efficient heat transfer. Over time—typically 2–5 years—paste can dry out and lose effectiveness, leading to higher temperatures and reduced performance. Gamers, overclockers, and anyone noticing rising temps under load should consider reapplying it.
Start by shutting down your PC, unplugging it, and grounding yourself. Remove the cooler from the CPU or GPU, then clean off the old paste using isopropyl alcohol (90% or higher) and a lint-free cloth or coffee filter. Apply a small, pea-sized amount of new paste to the center of the chip. When the cooler is reattached and pressure is applied, the paste will spread evenly across the surface.
Too much paste can insulate rather than conduct heat, while too little can leave air pockets. High-quality pastes like Arctic MX-6, Noctua NT-H1, or Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut offer excellent thermal performance and longevity.
For a detailed walkthrough, including application patterns, brand comparisons, and troubleshooting, see our How to Replace Thermal Paste guide.
Updating BIOS safely
This one also comes with some risks and is not something you should worry about unless your system is old enough, and if you’re running into BIOS related issues.
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI firmware controls the hardware initialization process before your operating system loads. Updating it can add hardware compatibility, fix stability issues, and improve performance—but it’s not something to do casually. A failed or interrupted BIOS update can render your motherboard unusable.
Before updating, verify the exact model and revision of your motherboard, then check the manufacturer’s website for the latest firmware. Read the release notes to ensure the update addresses an issue relevant to you, such as CPU support or bug fixes. If your system is stable and the update doesn’t provide a clear benefit, it’s often best to leave it as is.
When you do update, follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely. Most modern boards offer a built-in flashing utility accessible from the BIOS menu, allowing you to update from a USB drive without booting into Windows. Ensure the PC won’t lose power during the process—ideally, use a UPS.
For full instructions, screenshots, and troubleshooting tips, see our Updating BIOS Safely guide.
Organizing cables for better airflow
Cable management isn’t just about aesthetics—it has a direct impact on airflow, dust accumulation, and ease of future upgrades. Tangled or poorly routed cables can block fan intakes and exhaust paths, causing heat pockets inside the case. Over time, this can lead to higher temperatures, more dust buildup, and reduced component lifespan.
Start by unplugging your PC and planning cable routes before making any adjustments. Most modern cases have cable cutouts and channels behind the motherboard tray—use these to keep cables hidden and out of airflow paths. Secure them with zip ties, Velcro straps, or reusable twist ties for easy adjustments later.
Group cables by function (e.g., all front-panel connectors together, all SATA cables together) to minimize crossing paths. Keep power supply cables flat against the case wall, and avoid wrapping them tightly around components where they could obstruct airflow. If your PSU is modular, only connect the cables you need to reduce clutter.
For examples of clean layouts, cable routing diagrams, and tool recommendations, see our Organizing Cables for Better Airflow guide.
Preventive measures
Good PC maintenance also means preventing problems before they start. Environmental factors, power stability, and daily habits all play a role in keeping your system healthy.
Start with proper power protection. A surge protector is the bare minimum to defend against sudden voltage spikes, but a UPS (uninterruptible power supply) offers better protection and gives you time to shut down safely during outages. This can prevent file corruption and hardware damage.
Ventilation is another key factor. Place your PC in an area with plenty of airflow and avoid pushing it against walls or inside enclosed cabinets without ventilation holes. Keep it away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
Avoid overloading electrical outlets or daisy-chaining power strips, as this increases fire risk and can cause inconsistent power delivery. If you live in a dusty environment, consider using dust filters on case intakes and cleaning them monthly.
Finally, handle your PC carefully during upgrades or cleaning. Static discharge can silently damage components, so always ground yourself before touching internal parts. Preventive habits like these can save you from expensive repairs and downtime later.